foods that affect female fertility
Unfortunately or fortunately, the impact of food on women’s fertility is much greater than what has been addressed. Many cases of infertility can be traced back to dietary habits that have unfortunately become the norm worldwide. Without realizing it, we significantly diminish our body’s fertility potential with certain foods. While there is limited scientific evidence directly linking specific foods to infertility in females, certain dietary factors may have indirect effects on reproductive health. It’s important to note that individual circumstances and overall lifestyle play significant roles in fertility.
If you have plans for fertility in the near future, we recommend reading this article from SISIWAY and taking the restrictions on women’s conception seriously.
foods to avoid for female fertility
Here are 10 foods that affect female fertility:
-
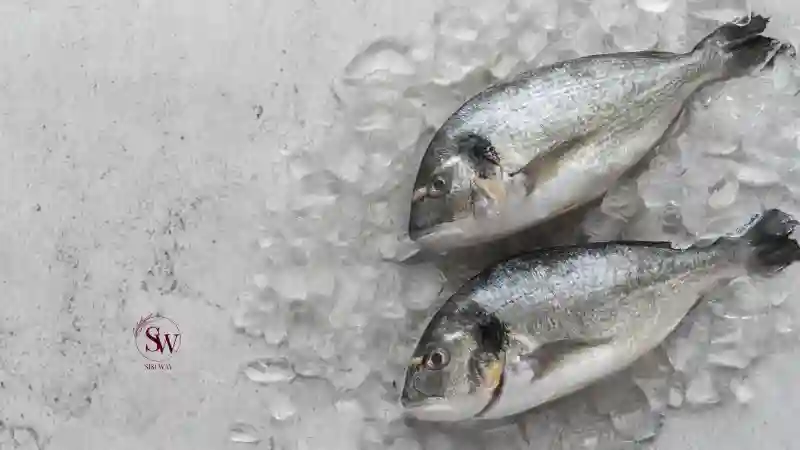
High-Mercury Fish
Fish with high levels of mercury, such as shark, swordfish, and king mackerel, should be consumed in limited quantities, as high levels of mercury can potentially affect fertility and harm the developing fetus.

-
Trans Fats
Foods high in trans fats, such as fried and processed foods, have been associated with inflammation and negative impacts on overall health. While their direct link to female infertility is not well-established, it’s generally advisable to limit trans fat intake for overall well-being. Here are some examples of foods that may contain trans fats:
- Margarine (particularly stick margarine)
- Shortening
- Deep-fried foods (e.g., french fries, fried chicken, doughnuts)
- Processed snacks (e.g., potato chips, crackers, microwave popcorn)
- Packaged baked goods (e.g., cakes, cookies, pastries)
- Store-bought pie crusts and dough
- Non-dairy creamers
- Fast food items (e.g., hamburgers, fried chicken sandwiches)
- Commercially prepared frosting and icing
- Some frozen pizzas
-
High Glycemic Index (GI) Foods
Foods with a high GI, including refined carbohydrates like white bread, white rice, and sugary snacks, can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. This can lead to insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances, potentially affecting fertility. Here are some examples of high glycemic index (GI) foods:
- White bread
- White rice
- Cornflakes
- Instant oatmeal
- Baked potatoes
- Pretzels
- Rice cakes
- Watermelon
- Pineapple
- Raisins
- Dates
- Soda and sugary drinks
- Jelly beans
- Cookies and cakes made with refined flour and sugar
- Processed breakfast cereals with added sugars

-
Excessive Alcohol
Heavy alcohol consumption has been associated with menstrual irregularities, disruptions in hormone production, and decreased fertility in females. It’s generally recommended to limit alcohol intake or avoid it altogether when trying to conceive.

-
Caffeine
While moderate caffeine consumption is generally considered safe, high caffeine intake has been associated with delayed conception and increased risk of miscarriage. It’s advisable to limit caffeine intake to moderate levels (usually less than 200 mg per day) when trying to conceive. Here are some examples of common sources of caffeine:
- Coffee: Brewed coffee, espresso, instant coffee, and coffee-based beverages like lattes and cappuccinos.
- Tea: Black tea, green tea, oolong tea, white tea, and herbal teas that contain caffeine, such as yerba mate and guayusa.
- Energy Drinks: Many energy drinks contain high levels of caffeine, along with other stimulants and additives.
- Soft Drinks: Some carbonated beverages, like cola drinks, contain caffeine.
- Chocolate: Dark chocolate and milk chocolate contain varying amounts of caffeine.
- Cocoa Powder: Cocoa powder used in hot chocolate, baking, and desserts can contain caffeine.
- Some Medications: Certain over-the-counter medications, such as headache remedies and cold/flu medications, may include caffeine.
- Some Weight Loss Supplements: Certain weight loss supplements and dietary aids may contain caffeine or other stimulants.
- Some Pre-Workout Supplements: Pre-workout supplements used for exercise performance enhancement may contain caffeine.

-
Soy Products
Soy contains compounds known as phytoestrogens, which have estrogen-like effects in the body. High levels of estrogen can potentially disrupt hormonal balance and interfere with fertility. While moderate soy consumption is generally considered safe, excessive intake may be a concern for some individuals. Here are some examples of soy products:
- Tofu: Tofu, also known as bean curd, is a popular soy-based protein source made from curdling soy milk and pressing it into solid blocks with varying textures (firm, soft, silken).
- Edamame: Edamame refers to young, green soybeans that are harvested before they fully mature. They are often boiled or steamed and can be enjoyed as a snack or added to various dishes.
- Soy Milk: Soy milk is a plant-based milk alternative made by soaking, grinding, and boiling soybeans. It is commonly used as a dairy milk substitute.
- Soy Sauce: Soy sauce is a condiment made from fermented soybeans, wheat (or gluten-free alternatives), water, and salt. It is commonly used in Asian cuisine as a flavor enhancer.
- Tempeh: Tempeh is a traditional Indonesian food made from fermented soybeans, formed into a firm, compact cake. It has a nutty flavor and a firm texture.
- Miso: Miso is a traditional Japanese seasoning made by fermenting soybeans with salt and a fungus called koji. It is commonly used in soups, marinades, and dressings.
- Soy-based Burgers and Meat Alternatives: There are various soy-based burgers, veggie patties, sausages, and other meat alternatives available that use soy protein as a primary ingredient.
- Soy-based Snacks: Soy-based snacks, such as soy crisps or soy-based protein bars, are available as convenient, on-the-go options.
- Soy-based Yogurt: Soy-based yogurt is a dairy-free alternative made from soy milk and fermented with yogurt cultures.
- Soy-based Ice Cream: Soy-based ice cream is a non-dairy frozen dessert made from soy milk.

-
Low-Fat Dairy
Some studies have suggested a possible link between high intake of low-fat dairy products and an increased risk of ovulatory infertility. However, more research is needed to establish a definitive relationship.

-
Processed Meats
Processed meats, such as sausages, hot dogs, and deli meats, often contain nitrates and high levels of saturated fats. While their direct impact on female infertility is not well-established, these foods are generally considered unhealthy and should be consumed in moderation.

-
Artificial Sweeteners
Some research has suggested a potential link between artificial sweeteners and decreased fertility. However, more studies are needed to confirm this association. It’s generally advisable to consume artificial sweeteners in moderation.

-
Low Iron Foods
Iron deficiency has been associated with ovulatory infertility. It’s important for women of reproductive age to consume adequate amounts of iron-rich foods like lean meats, beans, fortified cereals, and dark leafy greens.

In this table, you can see worst foods for female fertility
| Foods that cause infertility in females | examples |
| High-Mercury Fish | shark, swordfish and king mackerel |
| Trans Fats | Margarine, Shortening, Deep-fried foods, Processed snacks, Packaged baked goods, Store-bought pie crusts and dough, Non-dairy creamers, Fast food items, Commercially prepared frosting and icing, Some frozen pizzas |
| High Glycemic Index (GI) Foods | White bread, White rice, Cornflakes, Instant oatmeal, Baked potatoes, Pretzels, Rice cakes, sugary drinks |
| Excessive Alcohol | |
| Caffeine | Coffee, Tea, Energy Drinks, Soft Drinks, Chocolate, Cocoa Powder, Some Medications, Some Weight Loss Supplements, Some Pre-Workout Supplements |
| Soy Products | Tofu, Edamame, Soy Milk, Soy Sauce, Tempeh, Miso, Soy-based Burgers and Meat Alternatives, Soy-based Snacks,
Soy-based Yogurt, Soy-based Ice Cream |
| Low-Fat Dairy | |
| Processed Meats | sausages, hot dogs, and deli meats |
| Artificial Sweeteners | |
| Low Iron Foods |
It’s important to note that fertility is a complex issue influenced by various factors, including genetics, overall health, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical conditions. Maintaining a balanced diet, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals or fertility specialists are essential for optimizing reproductive health.
how does nutrition affect reproductive health?
Food can affect women’s fertility in several ways. Here are some ways in which food choices can impact female fertility:
Hormonal Balance and infertility in females
Certain foods can influence hormonal balance, which is crucial for regular menstrual cycles and ovulation. Imbalances in hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and insulin can interfere with ovulation and fertility. Consuming a diet high in processed foods, trans fats, and refined carbohydrates can disrupt hormone levels and increase the risk of conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and insulin resistance, which can negatively impact fertility.
Inflammation and infertility in females
A diet high in inflammatory foods can lead to chronic inflammation in the body. Inflammation can disrupt normal reproductive processes, impair egg quality, and interfere with implantation. Foods high in trans fats, processed sugars, and refined grains can contribute to inflammation, while a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help reduce inflammation and support fertility.
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance occurs when cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated insulin levels in the blood. This condition can disrupt hormone levels and interfere with ovulation. Foods with a high glycemic index, such as refined carbohydrates and sugary snacks, can trigger rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, leading to increased insulin production and potentially contributing to insulin resistance.
Weight and BMI and infertility in females
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for fertility. Both overweight and underweight conditions can disrupt hormonal balance and affect ovulation. Consuming a balanced diet that provides adequate nutrients and supports a healthy weight can promote regular menstrual cycles and improve fertility outcomes.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Certain nutrients are essential for reproductive health and fertility. For example, folate, iron, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids play critical roles in fertility and early pregnancy. A diet lacking in these nutrients can impact fertility and increase the risk of complications during pregnancy. Consuming a varied diet that includes a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help ensure adequate nutrient intake.
Environmental Contaminants and fertility in females
Some foods, particularly certain types of fish, may contain environmental contaminants like mercury and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), which can interfere with fertility. It’s important to choose fish low in mercury and limit exposure to other environmental toxins that can affect reproductive health.
It’s worth noting that individual responses to food can vary, and the impact of diet on fertility can differ from person to person. Working with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian who specializes in fertility can provide personalized guidance and support in optimizing dietary choices for improved fertility.
Conclusion
While no single food is solely responsible for fertility issues, maintaining a healthy diet can significantly impact reproductive health. By avoiding or minimizing the consumption of the worst foods for female fertility, women can optimize their chances of conceiving and promote overall well-being. Prioritizing whole, unprocessed foods, rich in essential nutrients, and maintaining a healthy weight can contribute to a more favorable reproductive environment. If you have concerns about your fertility or are planning for pregnancy, it’s always beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.