Gluten is a protein composite found in wheat and related grains like barley, rye, and oats. It plays a crucial role in giving dough its elasticity and helps it rise and maintain its shape. While gluten is a staple in many diets worldwide, it has garnered attention in recent years due to its potential impact on health, particularly for individuals with celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
The Composition of Gluten
Gluten is comprised of two main proteins: glutenin and gliadin. These proteins are responsible for the unique properties of gluten that make it essential in baking. Glutenin provides elasticity, allowing the dough to stretch and rise, while gliadin contributes to the viscosity of the dough, giving it the ability to trap air bubbles and create a light, airy texture.
The Role of Gluten in Baking
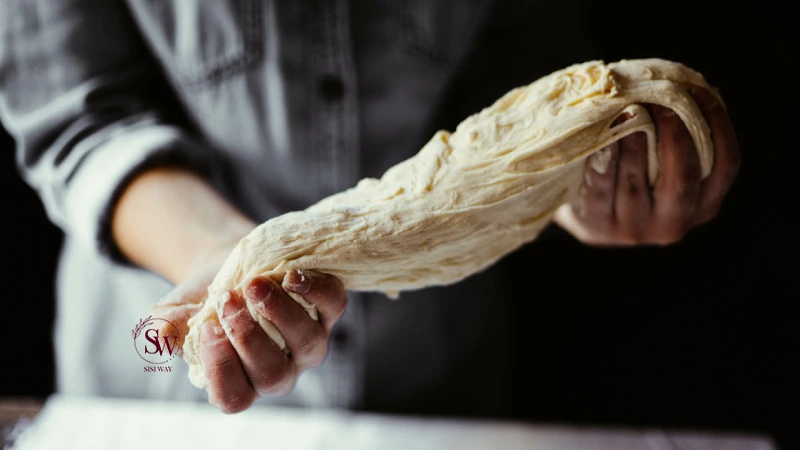

In baking, gluten plays a crucial role in the formation of the dough and the texture of the final product. When flour is mixed with water, the gluten proteins combine to form a network that traps air bubbles. This network gives the dough its elastic and stretchy properties, allowing it to rise when leavened with yeast or baking powder.
Gluten Sensitivity and Celiac Disease
For some individuals, gluten can trigger adverse reactions. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. This damage can interfere with the absorption of nutrients and lead to symptoms such as diarrhea, bloating, and fatigue.
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) is a condition in which individuals experience symptoms similar to those of celiac disease when consuming gluten but without the same autoimmune response. Symptoms of NCGS may include abdominal pain, bloating, and fatigue.
Gluten Intolerance
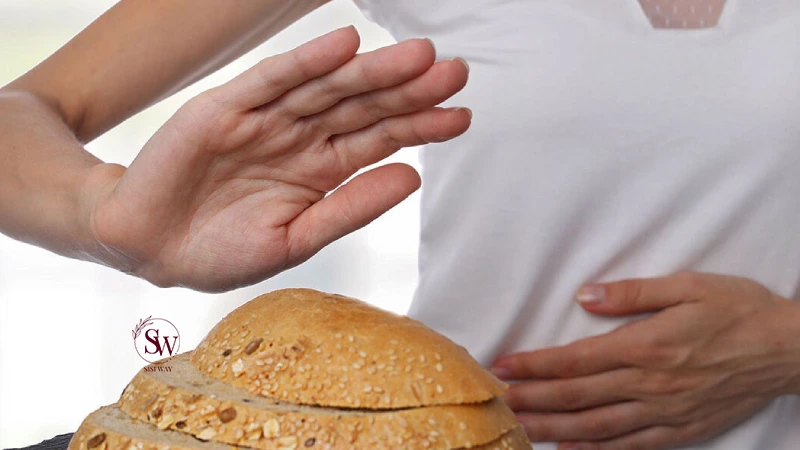

In addition to celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity, some individuals may experience gluten intolerance, which is a term used to describe a range of symptoms that occur after consuming gluten-containing foods. Unlike celiac disease, gluten intolerance does not involve an autoimmune response or damage to the small intestine.
Symptoms of gluten intolerance can vary widely and may include bloating, gas, diarrhea, fatigue, headache, and joint pain. However, the exact mechanisms underlying gluten intolerance are not well understood, and diagnosis can be challenging.
It’s important to note that gluten intolerance is different from celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity, and individuals experiencing symptoms should consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management plan.
Gluten-Free Diet

Due to the prevalence of celiac disease and the rise in gluten sensitivity awareness, many people are adopting gluten-free diets. A gluten-free diet excludes all sources of gluten, including wheat, barley, rye, and oats. Instead, individuals on a gluten-free diet can consume gluten-free grains and flour, such as rice, corn, quinoa, and almond flour.
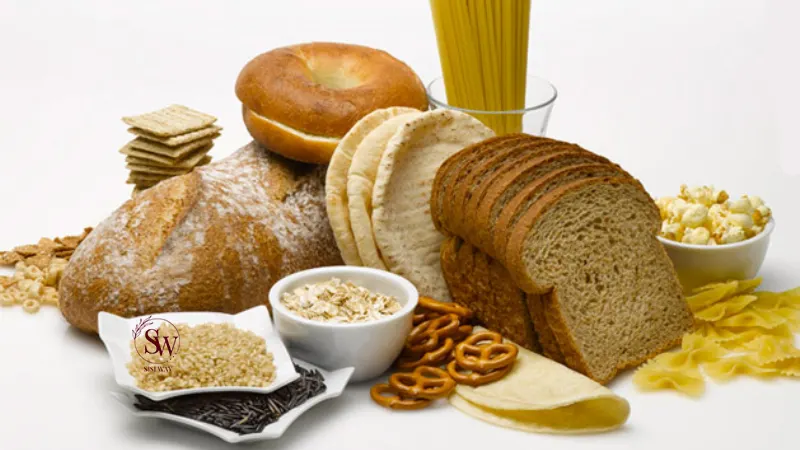
Foods That Contain Gluten
Gluten is commonly found in a variety of foods and ingredients. Here are some examples of foods that typically contain gluten:
- Wheat-based products: This includes bread, pasta, noodles, couscous, and flour tortillas.
- Barley: Barley is often used in malted products, such as malt vinegar and some beers.
- Rye: Rye bread and rye-based cereals are common sources of gluten.
- Oats: While oats themselves do not contain gluten, they are often processed in facilities that also handle wheat, barley, and rye, leading to potential cross-contamination.
- Processed foods: Many processed foods, such as soups, sauces, and condiments, may contain gluten as a thickening agent or filler.
- Baked goods: Cakes, cookies, pastries, and other baked goods are typically made with wheat flour, which contains gluten.
- Beer: Most beers are brewed with barley, which contains gluten.

Why Gluten Is Bad for Some People?
While gluten is safe for most people to consume, it can be problematic for individuals with certain conditions. Here’s why gluten can be considered “bad” for some:
- Celiac Disease: For individuals with celiac disease, gluten triggers an immune response that damages the lining of the small intestine. This damage can lead to malabsorption of nutrients, resulting in symptoms such as diarrhea, bloating, fatigue, and weight loss. Long-term complications of untreated celiac disease can include osteoporosis, infertility, and neurological disorders.
- Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS): Some individuals experience symptoms similar to those of celiac disease when consuming gluten but without the autoimmune response seen in celiac disease. This condition is known as non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS). Symptoms of NCGS can include abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and fatigue.
- Wheat Allergy: Wheat allergy is an allergic reaction to proteins found in wheat, including gluten. Symptoms of a wheat allergy can vary from mild (hives, itching) to severe (anaphylaxis) and can occur shortly after consuming wheat-containing products.
- Other Health Conditions: Some individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or other gastrointestinal conditions may experience symptom exacerbation when consuming gluten, although the exact mechanism is not fully understood.
FAQs
Is gluten harmful to everyone?
No, gluten is only harmful to individuals with celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity. For the general population, gluten is a safe and essential part of a balanced diet.
Can gluten-free products be consumed by everyone?
Yes, gluten-free products can be consumed by everyone, but they are primarily intended for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. It’s essential to read labels carefully, as some gluten-free products may still contain traces of gluten.
Are there health benefits to a gluten-free diet for those without gluten sensitivity?
There is no scientific evidence to suggest that a gluten-free diet provides health benefits for individuals without gluten sensitivity. In fact, eliminating gluten from the diet can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not properly managed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gluten is a complex protein found in wheat and related grains that plays a crucial role in baking. While essential for many baking processes, gluten can be harmful to individuals with celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity. For those individuals, following a gluten-free diet is necessary to avoid adverse health effects. However, for the general population, gluten is safe and can be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet.