What Are the Top 10 Lifestyle Diseases?

What Are Lifestyle Diseases
In today’s fast-paced world, the prevalence of lifestyle diseases has risen significantly. These diseases, often referred to as non-communicable diseases (NCDs), are primarily caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices. By understanding these diseases and adopting preventive measures, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the risk of developing them. In this article of sisiway, we will explore the top 10 lifestyle diseases and provide insights on how to prevent them through positive lifestyle changes.

-
Cardiovascular Disease:
Cardiovascular disease is a leading lifestyle disease that encompasses a range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. It is primarily caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices such as poor diet, sedentary behavior, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and chronic stress. These factors contribute to the development of risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, obesity, and diabetes, which increase the likelihood of cardiovascular disease.
Preventing cardiovascular disease requires a comprehensive approach to lifestyle modifications. Adopting a heart-healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help reduce the risk. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises and strength training, strengthens the heart and improves circulation. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake are crucial steps in preventing cardiovascular disease. Additionally, managing stress through techniques like mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and seeking support can have a positive impact on cardiovascular health. By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing cardiovascular disease and improve their overall heart health.

-
Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes is a prevalent lifestyle disease characterized by high blood sugar levels and insulin resistance. It is strongly influenced by unhealthy lifestyle choices, including poor diet, sedentary behavior, and obesity. Consuming a diet high in processed and sugary foods, with limited intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Lack of regular physical activity and sedentary habits contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance, further exacerbating the disease.
Preventing type 2 diabetes revolves around adopting a healthy lifestyle. Making dietary changes such as consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats while limiting sugary and processed foods is crucial. Regular physical activity, including aerobic exercises and strength training, helps improve insulin sensitivity and maintain a healthy weight. Weight management plays a significant role in preventing type 2 diabetes, as excess body fat is closely linked to insulin resistance. By engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and making mindful choices about nutrition, individuals can lower their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and improve their overall health.
Also read: is type 2 diabetes preventable

-
Obesity:
Obesity is a prevalent lifestyle disease characterized by excessive body weight and an accumulation of body fat. It is primarily caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices such as a poor diet high in calories, sedentary behavior, and a lack of physical activity. Consuming a diet rich in processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-fat foods contributes to weight gain and obesity. Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle, marked by prolonged periods of sitting or inactivity, further exacerbates the risk of obesity.
Preventing and managing obesity requires adopting a holistic approach to lifestyle changes. Making dietary modifications, such as reducing calorie intake, choosing nutrient-dense foods, and practicing portion control, is crucial in preventing obesity. Regular physical activity is essential for weight management and overall health. Engaging in moderate-intensity aerobic exercises, strength training, and incorporating more movement into daily routines can help burn calories and maintain a healthy weight. Additionally, developing healthy habits like mindful eating, stress management, and getting adequate sleep contribute to preventing obesity. By making sustainable changes to diet and physical activity patterns, individuals can reduce their risk of obesity and improve their overall well-being.

-
Cancer:
Cancer, although influenced by a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors, can also be considered a lifestyle disease. Certain lifestyle choices can significantly impact the risk of developing various types of cancer. For example, tobacco use, including smoking and exposure to second-hand smoke, is a leading cause of lung cancer and increases the risk of other types of cancer, such as throat, mouth, and bladder cancer. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption is linked to an increased risk of developing liver, breast, colorectal, and other types of cancer.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of cancer. A nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients, antioxidants, and phytochemicals that protect against cancer. Limiting the consumption of processed and red meats, sugary foods, and beverages can also contribute to cancer prevention. Engaging in regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces the risk of certain cancers, including breast, colon, and prostate cancer. It is also important to undergo recommended cancer screenings, such as mammograms, Pap smears, and colonoscopies, as early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes. By making informed choices and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can lower their risk of developing cancer and promote overall well-being.
-
Chronic Respiratory Diseases:
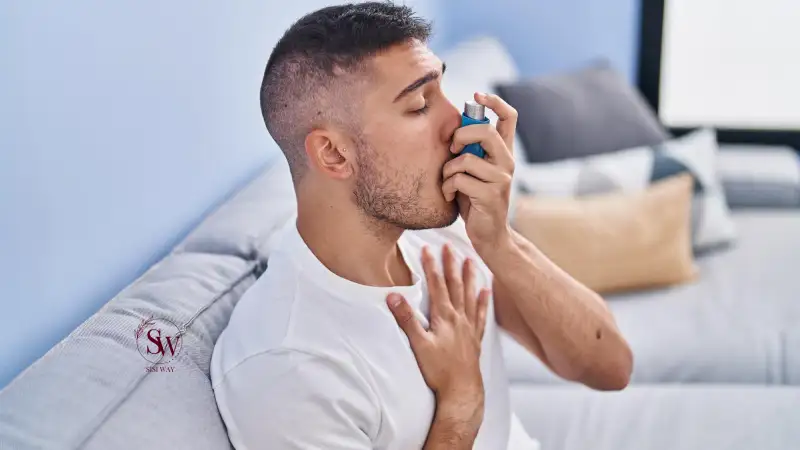
Chronic respiratory diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, can be considered lifestyle diseases as they are influenced by certain lifestyle choices and environmental factors. Smoking is a primary risk factor for the development of COPD, as well as other respiratory conditions. Prolonged exposure to second-hand smoke and environmental pollutants, such as air pollution and occupational hazards, can also contribute to chronic respiratory diseases. Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle and poor nutrition can weaken the respiratory system, making individuals more susceptible to respiratory conditions.
Preventing chronic respiratory diseases involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and minimizing exposure to respiratory irritants. Quitting smoking is paramount in preventing and managing respiratory diseases. Avoiding exposure to second-hand smoke and reducing exposure to air pollutants are also essential. Engaging in regular physical activity helps improve lung function and strengthens the respiratory muscles. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides the necessary nutrients to support respiratory health. Practicing good respiratory hygiene, such as covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, can help prevent the spread of respiratory infections. By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic respiratory diseases and improve their lung health.

-
Liver Disease:
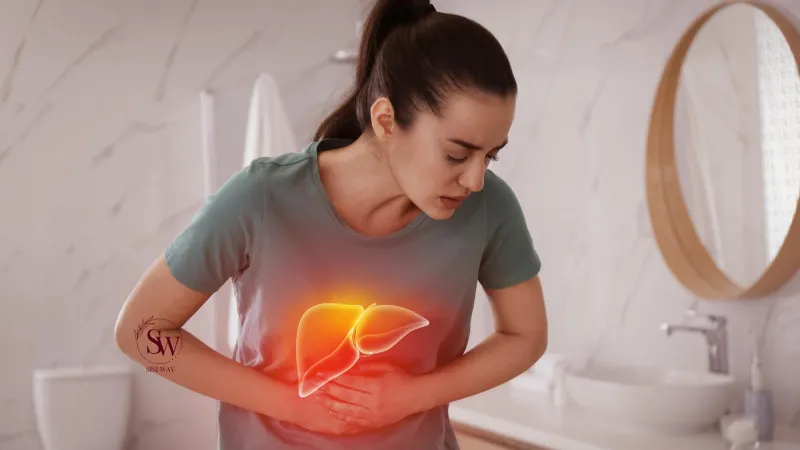
Liver disease, including conditions such as fatty liver disease and cirrhosis, can be considered lifestyle diseases due to their close association with certain lifestyle choices and habits. Excessive alcohol consumption is a leading cause of liver disease, particularly alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol abuse can lead to inflammation, scarring, and damage to the liver cells, impairing its ability to function properly. In addition to alcohol, an unhealthy diet high in saturated fats, sugar, and processed foods can contribute to the development of fatty liver disease, a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. Obesity, which often results from a sedentary lifestyle and poor dietary choices, is also a significant risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Preventing liver disease involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and making conscious choices that support liver health. Limiting or avoiding alcohol consumption is crucial in preventing alcoholic liver disease. Following a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while minimizing the consumption of unhealthy fats and added sugars helps maintain liver health. Regular physical activity helps manage weight and reduces the risk of fatty liver disease. It is also important to practice safe behaviors, such as practicing safe sex and avoiding sharing needles, to prevent the transmission of viral hepatitis, which can cause severe liver damage. By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can protect their liver and reduce the risk of developing liver disease.

-
Kidney Disease:
Kidney disease, particularly chronic kidney disease (CKD), is strongly influenced by lifestyle choices and behaviors. Several lifestyle factors contribute to the development and progression of kidney disease. Uncontrolled diabetes and high blood pressure are leading causes of kidney disease. These conditions often result from poor dietary choices, sedentary behavior, and obesity. A diet high in sodium, saturated fats, and processed foods can contribute to high blood pressure and diabetes, both of which can damage the kidneys over time. Additionally, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and the prolonged use of certain medications can also harm kidney function and increase the risk of kidney disease.
Preventing kidney disease involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying conditions. Managing diabetes and high blood pressure through medication, regular monitoring, and lifestyle modifications is crucial in preventing kidney disease. Following a balanced diet that is low in sodium, processed foods, and unhealthy fats, while incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can support kidney health. Engaging in regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, manage blood pressure, and improve overall cardiovascular health, all of which benefit the kidneys. Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding smoking are also important in preserving kidney function. By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing kidney disease and protect their kidney health.
-
Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones, can be considered a lifestyle disease due to its close association with certain lifestyle choices and habits. A sedentary lifestyle devoid of weight-bearing exercises and physical activity can contribute to the development of osteoporosis. Regular exercise, particularly weight-bearing exercises like walking, jogging, and strength training, helps stimulate bone growth and maintain bone density. On the other hand, a lack of physical activity can lead to bone loss and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Dietary choices also play a significant role in the development of osteoporosis. Inadequate intake of calcium and vitamin D, essential nutrients for bone health, can weaken bones and increase the risk of fractures. A diet lacking in dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and other calcium-rich foods can contribute to calcium deficiency and osteoporosis. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can negatively affect bone health and increase the risk of osteoporosis. By adopting a lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and avoiding harmful habits, individuals can reduce their risk of developing osteoporosis and promote stronger bones.
-
Mental Health Disorders:
Mental health disorders, while influenced by various factors, can also be understood as lifestyle diseases due to the significant impact of lifestyle choices on mental well-being. Unhealthy lifestyle habits such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, chronic stress, and inadequate sleep can contribute to the development and exacerbation of mental health disorders. A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can negatively affect brain health and contribute to mood disorders like depression and anxiety. Sedentary behavior and a lack of exercise can lead to decreased production of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters, and can contribute to feelings of lethargy and low mood.
Furthermore, chronic stress, often associated with a fast-paced, demanding lifestyle, can take a toll on mental health. High levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol, over an extended period can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders. Inadequate sleep or poor sleep quality can also impact mental well-being. Sleep deprivation can disrupt mood regulation, cognitive function, and overall mental health. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management techniques, and prioritizing sufficient sleep can significantly contribute to the prevention and management of mental health disorders. By making lifestyle choices that prioritize mental well-being, individuals can enhance their overall mental health and resilience.
Also read: How to Manage Stress and Anxiety?
-
Alzheimer’s Disease:
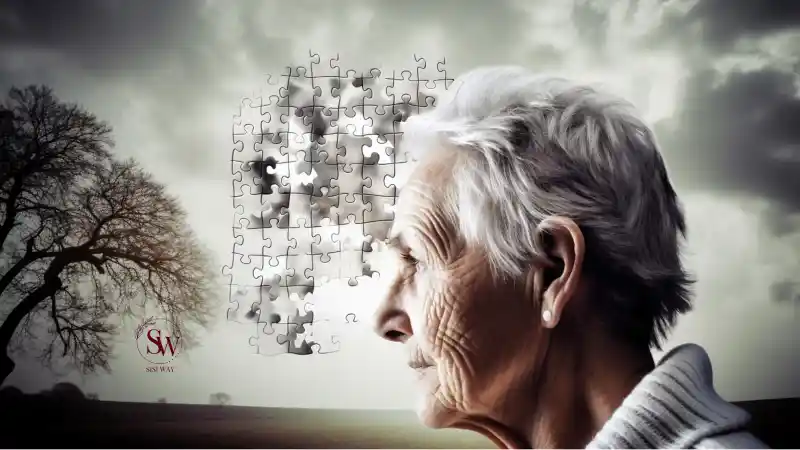
Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, is primarily influenced by genetic and age-related factors. However, emerging research suggests that certain lifestyle choices and habits can impact the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Unhealthy lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and chronic conditions like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease have been associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can play a role in reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, such as the Mediterranean diet, has been associated with a lower risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. Engaging in regular physical exercise, including aerobic activities and strength training, promotes brain health and reduces the risk of cognitive impairment. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to a decreased risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, managing chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease through lifestyle modifications and appropriate medical care can help reduce the risk of cognitive decline. While lifestyle choices cannot guarantee the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease, they can contribute to overall brain health and potentially reduce the risk or delay the onset of the disease.

FAQ
- What are the top lifestyle diseases?
The top lifestyle diseases include cardiovascular diseases (such as heart disease and stroke), type 2 diabetes, obesity, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, liver disease, kidney disease, osteoporosis, and mental health disorders.
- What are the main causes of lifestyle diseases?
Lifestyle diseases are primarily caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices and behaviors. These include poor dietary habits, sedentary behavior and lack of physical activity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, chronic stress, inadequate sleep, and exposure to environmental pollutants
- Can lifestyle diseases be prevented?
Yes, many lifestyle diseases can be prevented or their risk reduced by adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes making dietary changes, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, managing stress effectively, maintaining a healthy weight, getting adequate sleep, and practicing preventive measures.
- Are lifestyle diseases reversible?
In some cases, lifestyle diseases can be reversible or their progression can be slowed down through lifestyle modifications.
Conclusion:
Preventing lifestyle diseases requires a proactive approach towards adopting healthy lifestyle choices. By incorporating regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress levels, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, and prioritizing mental health, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing these top 10 lifestyle diseases. Empowering ourselves with knowledge and taking action today can lead to a healthier and more fulfilling life in the long run. Remember, prevention is always better than cure.



