Vitamins to Boost Fertility

Vitamins to Get Pregnant Fast
When it comes to enhancing fertility, a holistic approach that includes proper nutrition is essential. While a balanced diet should be the primary source of nutrients, certain vitamins play a crucial role in supporting reproductive health and increasing the chances of conception. In this article of sisiway, we will explore some key vitamins known for their potential to boost fertility and discuss their importance in optimizing reproductive function.

-
Folic Acid (Vitamin B9):
Folic acid is a vital nutrient for women looking to conceive. It helps in the development of the neural tube in the early stages of pregnancy, reducing the risk of neural tube defects in the fetus. It is recommended that women of childbearing age consume 400-800 micrograms of folic acid daily. Good dietary sources of folic acid include leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, beans, and fortified cereals. Additionally, prenatal vitamins often contain folic acid, providing an additional source of this crucial nutrient.
Read more: How to Boost Fertility in Your 30s?

Here is a list of natural food sources that are rich in folic acid (Vitamin B9):
- Leafy Green Vegetables: Spinach, kale, collard greens, mustard greens, and Swiss chard are excellent sources of folic acid.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, kidney beans, and pinto beans are all high in folic acid.
- Citrus Fruits: Oranges, grapefruits, lemons, and limes provide a good amount of folic acid.
- Avocado: This creamy fruit is not only delicious but also a natural source of folic acid.
- Broccoli: This cruciferous vegetable is packed with folic acid and other essential nutrients.
-
Vitamin D:
Vitamin D is not only essential for bone health but also plays a role in fertility. Research suggests that vitamin D deficiency may be associated with menstrual irregularities and decreased fertility. Adequate levels of vitamin D in the body are linked to improved egg quality and increased chances of successful conception. Natural sources of vitamin D include sunlight exposure and certain foods like fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks. However, it may be challenging to obtain sufficient vitamin D from diet alone, and supplementation under medical guidance might be necessary. If you would like to obtain more detailed information about this topic, be sure to refer to the article “How Much Vitamin D is Essential for Women’s Health?“

Here is a list of natural food sources and other natural sources of Vitamin D:
- Sunlight: The sun is the most significant natural source of vitamin D. When your skin is exposed to sunlight, it produces vitamin D naturally. Spending time outdoors, especially during midday when the sun is strongest, can help increase your vitamin D levels.
- Fatty Fish: Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are excellent sources of vitamin D. Consuming these fish a few times a week can help boost your vitamin D intake.
- Cod Liver Oil: Cod liver oil is derived from the liver of codfish and is a rich source of vitamin D. It is available in supplement form and can provide a significant amount of vitamin D.
- Egg Yolks: Egg yolks contain small amounts of vitamin D. Including eggs in your diet, particularly the yolks, can contribute to your vitamin D intake.
- Fortified Dairy Products: Certain dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese are often fortified with vitamin D. Check the labels to ensure they are fortified with vitamin D.
-
Coenzyme Q10:
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is an antioxidant that plays a crucial role in cellular energy production. It is found in every cell in the body and is particularly abundant in the ovaries. CoQ10 levels decline with age, which may impact egg quality and overall fertility. Supplementation with CoQ10 has been shown to improve ovarian function, increase the number of high-quality eggs, and enhance fertility outcomes in women trying to conceive. The recommended dosage of CoQ10 varies, but typically ranges from 100-300 milligrams per day. As always, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.

Here is a list of natural food sources that contain Coenzyme Q10:
- Organ meats: Organ meats such as liver, heart, and kidney are particularly rich in Coenzyme Q10.
- Fatty Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, trout, and sardines contain moderate amounts of Coenzyme Q10.
- Meat: Beef, pork, and chicken also contain some Coenzyme Q10, although in smaller amounts compared to organ meats.
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds, especially peanuts, sesame seeds, and pistachios, contain Coenzyme Q10.
- Soybean and Canola Oil: These oils are plant-based sources of Coenzyme Q10 and can be used for cooking or salad dressings.
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are essential fats that support overall health and are beneficial for fertility. These fatty acids play a role in regulating hormonal balance, reducing inflammation, and improving blood flow to the reproductive organs. Including sources of omega-3 fatty acids in the diet, such as fatty fish (salmon, sardines), chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts, may promote reproductive health and increase the chances of successful conception.
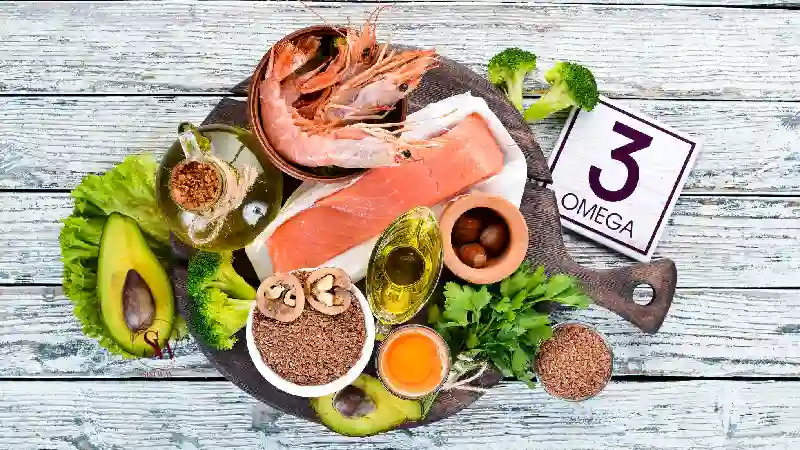

Here is a list of natural food sources that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids:
- Fatty Fish: Fatty fish are among the best sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Examples include salmon, mackerel, sardines, trout, and tuna.
- Flaxseeds and Flaxseed Oil: Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil are plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Ground flaxseeds can be added to smoothies, yogurt, or baked goods, while flaxseed oil can be used as a dressing or added to dishes after cooking.
- Chia Seeds: Chia seeds are another plant-based source of omega-3 fatty acids. They can be sprinkled over cereals, added to smoothies, or used as an egg substitute in baking.
- Walnuts: Walnuts are nuts that contain a good amount of omega-3 fatty acids. They can be eaten as a snack or added to salads, oatmeal, or baked goods.
- Hemp Seeds and Hempseed Oil: Hemp seeds and hempseed oil are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Hemp seeds can be sprinkled over salads, added to smoothies, or used in baking, while hempseed oil can be used as a dressing or drizzled over dishes.
-
Vitamin C:
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the reproductive cells from oxidative stress and damage. It also plays a role in hormone synthesis and supports the overall health of the reproductive system. Adequate levels of vitamin C have been associated with improved fertility in both men and women. Incorporate vitamin C-rich foods into your diet, such as citrus fruits, berries, kiwi, bell peppers, and broccoli. Alternatively, you can consider taking a vitamin C supplement under the guidance of a healthcare professional.

Here is a list of natural food sources that are rich in vitamin C:
- Citrus Fruits: Oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits, and tangerines are well-known for their high vitamin C content.
- Berries: Strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are all excellent sources of vitamin C.
- Kiwi: Kiwi is a small fruit that is packed with vitamin C.
- Papaya: Papaya is a tropical fruit that is rich in vitamin C.
- Guava: Guava is another tropical fruit that provides a significant amount of vitamin C.
-
Vitamin E:
Vitamin E is another important antioxidant that supports fertility by protecting reproductive cells from oxidative damage. It also helps maintain hormonal balance and supports healthy blood flow to the reproductive organs. Good dietary sources of vitamin E include nuts, seeds, spinach, and vegetable oils. Including these foods in your diet can help ensure sufficient intake of this vital nutrient.
Also read: What Causes Period Delay?

Here is a list of natural food sources that are rich in vitamin E:
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, hazelnuts, sunflower seeds, and peanuts are all good sources of vitamin E.
- Wheat Germ Oil: Wheat germ oil is one of the richest sources of vitamin E.
- Avocado: Avocado is a fruit that contains vitamin E along with healthy fats.
- Spinach: Spinach is a leafy green vegetable that provides vitamin E along with other beneficial nutrients.
- Swiss Chard: Swiss chard is another leafy green that is high in vitamin E.
-
Vitamin B12:
Vitamin B12 is essential for reproductive health as it plays a role in the production of genetic material and the development of red blood cells. Deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to irregular menstrual cycles and decreased fertility. Good dietary sources of vitamin B12 include animal products such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy. If you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, consider fortified plant-based foods or a B12 supplement to meet your needs.

Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-based food sources. Here is a list of natural food sources that are rich in vitamin B12:
- Shellfish: Clams, mussels, and oysters are particularly high in vitamin B12.
- Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, trout, and tuna contain vitamin B12.
- Meat: Beef, lamb, pork, and poultry are good sources of vitamin B12.
- Organ Meats: Liver, kidneys, and other organ meats are high in vitamin B12.
- Eggs: Eggs, especially the yolks, contain vitamin B12.
-
Iron:
Iron is crucial for fertility as it helps transport oxygen throughout the body, including the reproductive organs. Adequate iron levels are important for healthy ovulation and implantation of the fertilized egg. Good dietary sources of iron include lean meats, poultry, fish, legumes, spinach, and fortified cereals. It is important to note that iron absorption is enhanced when consumed with vitamin C-rich foods, so consider pairing iron-rich foods with citrus fruits or bell peppers.
Iron is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in the body’s oxygen transport and other important functions. Here is a list of natural food sources that are rich in iron:
- Red Meat: Beef, lamb, and pork are excellent sources of heme iron, which is highly absorbable by the body.
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey, especially the darker meat, contain good amounts of iron.
- Organ Meats: Liver, kidney, and heart are particularly high in iron.
- Seafood: Shellfish, such as clams, mussels, and oysters, are rich in iron. Fish like sardines and tuna also provide iron.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and soybeans are all good sources of iron.
Remember, while vitamins can support fertility, they should not replace a well-balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional or fertility specialist before starting any new supplements to ensure they are appropriate for your specific needs and medical history. By combining proper nutrition, lifestyle modifications, and medical guidance, you can optimize your fertility and increase your chances of achieving a healthy pregnancy.
Vitamins to Boost Fertility for Female
Folic Acid (Vitamin B9) is considered one of the most important vitamins to boost fertility in females. It plays a crucial role in the development of the neural tube in the early stages of pregnancy and helps reduce the risk of neural tube defects in the fetus. Folic acid is essential for women who are trying to conceive or planning to become pregnant. It is recommended that women of childbearing age consume adequate amounts of folic acid through a balanced diet or supplements to support reproductive health and increase the chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Vitamins to Boost Fertility for Male
One of the most important vitamins to boost fertility in males is Vitamin C. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps protect sperm cells from oxidative stress and damage. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and quality of sperm. Adequate levels of Vitamin C have been associated with improved sperm count, motility, and overall sperm health. Good dietary sources of Vitamin C include citrus fruits, berries, kiwi, bell peppers, and broccoli. By ensuring sufficient intake of Vitamin C, men can support their fertility and increase the chances of successful conception.

FAQ
- Can vitamins alone boost fertility?
While vitamins play a crucial role in supporting reproductive health, they are not a guaranteed solution for fertility issues. A balanced diet, healthy lifestyle, and medical guidance are equally important factors in optimizing fertility.
- How long does it take for vitamins to boost fertility?
The time it takes for vitamins to have an impact on fertility can vary. It is recommended to consistently incorporate vitamins into your routine for several months to allow for their potential benefits to take effect.
- Should I consult a healthcare professional before taking fertility-boosting vitamins?
Yes, it is highly advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or fertility specialist before starting any new supplements. They can assess your specific needs, provide personalized recommendations, and ensure the vitamins are appropriate for your individual circumstances.
Conclusion:
While vitamins alone cannot guarantee fertility, they can contribute significantly to reproductive health and optimize the chances of conception. Folic acid, vitamin D, CoQ10, and omega-3 fatty acids are among the key vitamins known for their potential to boost fertility. However, it is crucial to remember that individual needs may vary, and it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements. By combining proper nutrition, a healthy lifestyle, and personalized medical guidance, individuals can enhance their fertility potential and embark on their journey towards parenthood with optimism and well-being.
Read more: When is a Woman Most Fertile?