In the realm of women’s health, urinary tract infections (UTIs) stand out as a common yet often misunderstood ailment. This article delves into the intricacies of UTIs, shedding light on their symptoms, causes, and treatment options, and dispelling myths surrounding gender-specific prevalence.
What are the Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection?

- Persistent Urge to Urinate:
- Frequent and strong urges to urinate are hallmark symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI).
- The urge may persist even after emptying the bladder.
- Burning Sensation During Urination:
- A common discomfort associated with UTIs is a burning or painful sensation during urination.
- This sensation may be felt throughout the entire process of urination.
- Cloudy or Strong-Smelling Urine:
- Changes in the appearance and odor of urine are indicative of a potential UTI.
- Cloudiness or a strong, unpleasant smell may be noticeable.
- Pelvic Pain:
- UTIs can cause discomfort and pain in the pelvic region.
- The pain may range from mild to severe and can be persistent.
- Discomfort in the Lower Abdomen (Specifically in Women):
- Women may experience additional discomfort in the lower abdomen.
- This discomfort may be distinct from general pelvic pain.
- Traces of Blood in the Urine:
- In some cases, individuals with UTIs may observe traces of blood in their urine.
- Hematuria (blood in the urine) is a concerning symptom that requires medical attention.
- Variability in Symptom Intensity:
- It’s important to recognize that the intensity of these symptoms can vary from person to person.
- Some individuals may not experience all of these symptoms.
- Prompt Medical Attention:
- Recognizing the signs of a UTI and seeking medical attention promptly is crucial.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the spread of the infection and potential complications.
What Causes Urinary Tract Infection?
Understanding the root causes of urinary tract infections is paramount in developing effective prevention strategies. The majority of UTIs are caused by bacteria, with Escherichia coli (E. coli) being the primary culprit. This bacterium is normally present in the intestines but can find its way into the urethra and subsequently the urinary tract, leading to infection.
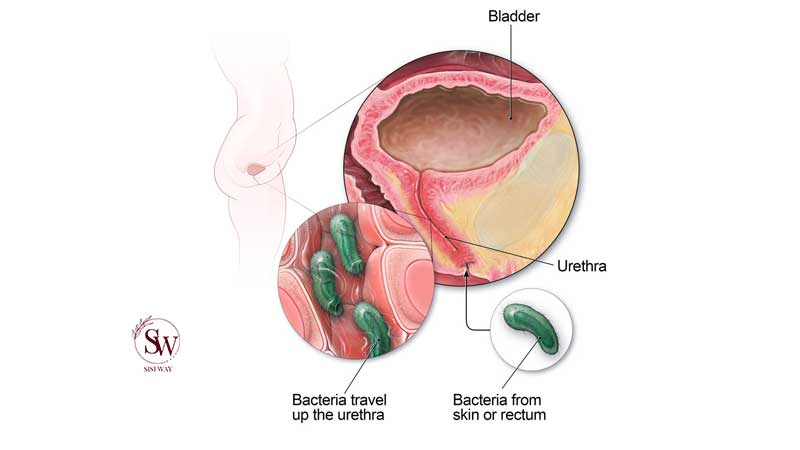
Several risk factors increase susceptibility to UTIs, including sexual activity, a weakened immune system, the use of certain types of birth control, and urinary tract abnormalities. Exploring these factors can empower women to make informed lifestyle choices that mitigate their risk of developing UTIs.
How to Treat an Urinary Tract Infection?
Prompt and appropriate treatment is essential when facing a urinary tract infection. Antibiotics are the primary course of action, and the specific choice depends on the type of bacteria causing the infection. It is imperative to complete the prescribed antibiotic course, even if symptoms alleviate before completion, to prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
In addition to medication, adopting healthy habits such as staying well-hydrated, avoiding irritants like caffeine and alcohol, and maintaining good personal hygiene can aid in the recovery process. For recurrent UTIs, a healthcare provider may recommend a more in-depth assessment to identify underlying causes.
What is the Best Antibiotic for Urinary Tract Infection?
Determining the best antibiotic for a urinary tract infection depends on the type of bacteria causing the infection and its susceptibility to different antibiotics. Commonly prescribed antibiotics for UTIs include trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, and ciprofloxacin. The choice of antibiotics is a decision made by healthcare professionals based on factors such as the patient’s medical history, allergies, and local antibiotic resistance patterns.
It is crucial for individuals not to self-prescribe antibiotics and instead consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Misuse of antibiotics contributes to the global issue of antibiotic resistance, posing a threat to public health.
Can Men Get Urinary Tract Infections?
While urinary tract infections are more prevalent in women due to the anatomical differences in their urinary tracts, men can also experience UTIs. The risk factors for men are often associated with age, an enlarged prostate, and sexual activity. However, the incidence of UTIs in men is significantly lower than in women.
Men experiencing symptoms such as pain or burning during urination, frequent urination, or cloudy urine should seek medical attention promptly. The diagnosis and treatment of UTIs in men may involve similar protocols as those for women.
Will an Urinary Tract Infection Go Away on Its Own?
Unlike some minor infections that may resolve without intervention, a urinary tract infection (UTI) typically requires medical attention and treatment. Without proper care, a UTI is unlikely to spontaneously disappear. Untreated UTIs can lead to more severe complications, such as kidney infections. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional promptly if symptoms suggestive of a UTI arise, ensuring timely diagnosis and appropriate intervention to promote swift recovery and prevent potential complications.
Frequently Asked Questions about Urinary Tract Infection:
- Are UTIs contagious?
No, UTIs are not contagious. They result from the entry of bacteria into the urinary tract, typically originating from the person’s digestive system. - Can UTIs be prevented?
Yes, adopting good hygiene practices, staying hydrated, urinating regularly, and avoiding irritants can reduce the risk of UTIs. Discussing risk factors with a healthcare provider can also guide personalized preventive measures. - Are cranberry products effective in preventing or treating UTIs?
While cranberry products have been traditionally associated with UTI prevention, scientific evidence on their efficacy remains inconclusive. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable for personalized advice. - Can UTIs lead to more severe complications?
If left untreated, UTIs can potentially lead to more serious kidney infections. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications. - Can Urinary Tract Infection Cause Bleeding?
Yes, urinary tract infections (UTIs) can, in some cases, lead to bleeding. Hematuria, the medical term for blood in the urine, may occur as a result of the irritation and inflammation caused by the infection. While not all individuals with UTIs experience bleeding, it is one of the potential symptoms. If someone notices blood in their urine or experiences any unusual symptoms, it is imperative to seek prompt medical attention for a thorough evaluation and appropriate management. - Is Urinary Tract Infection a Sexually Transmitted Disease?
No, a urinary tract infection (UTI) is not classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD). While sexual activity can contribute to the introduction of bacteria into the urethra, leading to a UTI, these infections are primarily caused by bacteria commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract. UTIs are not considered contagious or exclusively transmitted through sexual contact. However, certain sexual practices can increase the risk of UTIs in both men and women. If individuals are uncertain about the source of their symptoms, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate guidance.
In conclusion, understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for urinary tract infections empowers women to take proactive steps in managing their health. Seeking timely medical attention, adopting preventive measures, and dispelling common misconceptions contribute to a holistic approach to addressing this prevalent health concern.
Also read: What is a Dangerous Heart Rate for a Woman?