In the realm of nutritional supplements, magnesium stands out as a quiet hero, often overlooked amidst the flashy promises of other compounds. Yet, delve deeper, and you’ll uncover a mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, impacting everything from muscle function to heart health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unravel the mysteries surrounding magnesium, exploring its benefits, sources, and potential drawbacks.
Understanding Magnesium: A Vital Mineral
Magnesium, an essential mineral, serves as a cofactor for over 300 enzyme systems that regulate diverse biochemical reactions in the body. It’s involved in energy production, protein synthesis, muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and blood pressure regulation, among other functions. Despite its significance, studies estimate that nearly 50% of people in the United States and Europe consume less magnesium than recommended.
The Benefits of Magnesium:

- Promotes Heart Health: Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy heartbeat and regulating blood pressure. Research suggests that adequate magnesium intake may lower the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Supports Bone Health: Magnesium is essential for bone formation and density. It works alongside calcium and vitamin D to support bone health and prevent conditions like osteoporosis.
- Regulates Blood Sugar Levels: Magnesium helps regulate insulin secretion and glucose metabolism. Studies have shown that magnesium supplementation may improve insulin sensitivity in people with diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Eases Muscle Cramps and Spasms: Magnesium is vital for muscle function and relaxation. Adequate magnesium levels can help prevent and alleviate muscle cramps and spasms.
- Alleviates Anxiety and Depression: Some studies suggest that magnesium may have a calming effect on the nervous system, potentially reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Sources of Magnesium:
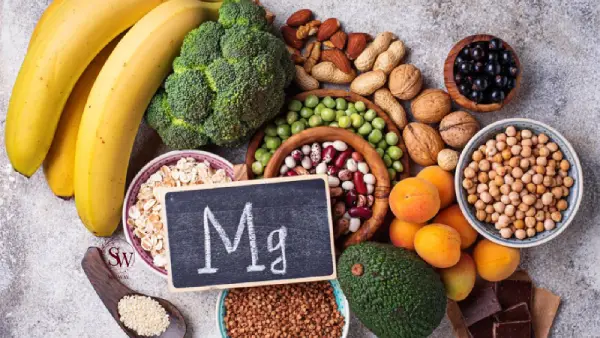
- Food Sources: Magnesium-rich foods include leafy greens (such as spinach and kale), nuts and seeds (such as almonds, pumpkin seeds, and cashews), whole grains (such as brown rice and oats), legumes (such as beans and lentils), and certain fish (such as salmon and mackerel).
- Supplements: Magnesium supplements are available in various forms, including magnesium oxide, magnesium citrate, magnesium glycinate, and magnesium chloride. The bioavailability of these forms may vary, with magnesium citrate and glycinate often being better absorbed than magnesium oxide.
Can Magnesium Help You Sleep?

In recent years, magnesium has gained attention for its potential role in promoting restful sleep. While the evidence is not yet conclusive, some studies suggest that magnesium may indeed play a role in improving sleep quality.
How Magnesium Impacts Sleep:
- Regulating Neurotransmitters: Magnesium is involved in the regulation of neurotransmitters, such as GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), which have calming effects on the brain. GABA helps to quiet the nervous system and promote relaxation, which is essential for falling asleep and staying asleep.
- Muscle Relaxation: Magnesium is known for its muscle-relaxing properties, which can help alleviate tension and promote physical relaxation. This relaxation of the muscles may contribute to a more comfortable and restful sleep experience.
- Regulating Circadian Rhythms: Magnesium plays a role in regulating the body’s internal clock, or circadian rhythms, which govern the sleep-wake cycle. By supporting the production of melatonin, the hormone that signals the body to prepare for sleep, magnesium may help regulate sleep patterns.
Can Magnesium Lower Blood Pressure?
Beyond its potential role in promoting sleep and overall health, magnesium has also been investigated for its impact on blood pressure regulation. High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease, making the exploration of natural interventions like magnesium particularly important.
The Relationship Between Magnesium and Blood Pressure:
- Vasodilation: Magnesium is involved in the regulation of vascular tone, or the constriction and dilation of blood vessels. It helps to relax blood vessels, promoting vasodilation, which can lead to lower blood pressure.
- Calcium Balance: Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance between calcium and magnesium levels within cells. This balance is essential for proper muscle function, including the smooth muscles that line blood vessels. Disruptions in this balance can contribute to increased vascular resistance and elevated blood pressure.
Should Magnesium Be Taken at Night?
One common question regarding magnesium supplementation is whether it’s best taken at night or during the day. While there isn’t a definitive answer, some individuals prefer taking magnesium before bedtime due to its potential calming and muscle-relaxing effects. As mentioned earlier, magnesium plays a role in promoting relaxation and supporting the production of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. Therefore, taking magnesium before bed may help enhance relaxation and promote a more restful night’s sleep for some individuals. However, it’s essential to consider individual preferences and sensitivities, as well as consult with a healthcare professional, as the timing of magnesium supplementation may vary depending on factors such as personal response and desired outcomes.
Should Magnesium Be Taken with Vitamin D?

The relationship between magnesium and vitamin D is an intriguing one, as both nutrients play essential roles in bone health and overall well-being. While there isn’t a strict requirement to take magnesium with vitamin D, some evidence suggests that the two may work synergistically to support optimal health outcomes. Vitamin D aids in the absorption and utilization of calcium, which is crucial for bone health, while magnesium contributes to bone mineralization and density. Additionally, magnesium is involved in the activation of vitamin D within the body, highlighting the potential interplay between these nutrients. Therefore, for individuals who are supplementing with vitamin D for bone health or other reasons, ensuring adequate magnesium intake may be beneficial. However, as with any supplementation regimen, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate approach based on individual needs and health status.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations:
While magnesium offers numerous health benefits, excessive intake from supplements can lead to gastrointestinal issues, such as diarrhea and abdominal cramping. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
- Can magnesium supplements interact with medications?
Yes, magnesium supplements can interact with certain medications, including antibiotics, diuretics, and medications for heart disease and diabetes. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before taking magnesium supplements, especially if you’re on medication. - How much magnesium should I take daily?
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for magnesium varies depending on age, sex, and other factors. For adult males, the RDA is around 400-420 mg per day, while for adult females, it’s around 310-320 mg per day. Pregnant and lactating women may require higher amounts. - Can magnesium help with migraines?
Some research suggests that magnesium supplementation may help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines, particularly in individuals with low magnesium levels. However, more studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness. - Are there any groups of people who may be at risk of magnesium deficiency?
Yes, certain groups, such as older adults, individuals with gastrointestinal diseases, and those with certain medical conditions (such as type 2 diabetes and chronic alcoholism), may be at higher risk of magnesium deficiency.
In conclusion, magnesium is a powerhouse mineral with a plethora of health benefits. From promoting heart health to supporting bone density and easing muscle tension, its impact on overall well-being cannot be overstated. By incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet and, if necessary, supplementing wisely, you can harness the remarkable benefits of this essential mineral for optimal health and vitality.