Everything About Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel Cell Carcinoma (MCC) is a rare but aggressive type of skin cancer that primarily affects older adults. Despite its rarity, the incidence of Merkel Cell Carcinoma has been steadily increasing over the past few decades, prompting a need for greater awareness and understanding of this disease. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various aspects of Merkel Cell Carcinoma, including its causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prognosis.
What is Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
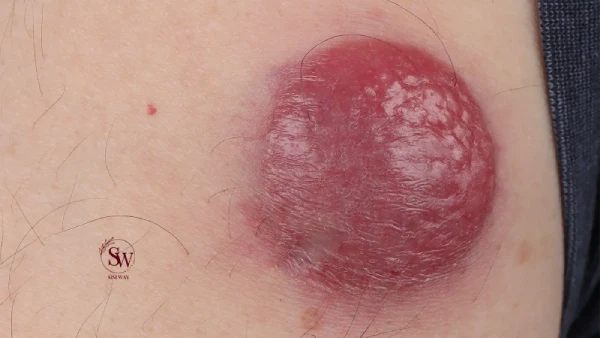
Merkel Cell Carcinoma is a type of neuroendocrine tumor that arises from Merkel cells, which are specialized cells found in the skin’s epidermis. These cells are responsible for the sense of touch. When these cells undergo malignant transformation, they can give rise to Merkel Cell Carcinoma. This cancer typically presents as a painless, firm nodule or lesion on the skin, most commonly on sun-exposed areas such as the head, neck, and arms.
Cause of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The exact cause of Merkel Cell Carcinoma is not fully understood. However, several risk factors have been identified, including:

- Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation Exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation from sunlight or tanning beds increases the risk of developing Merkel Cell Carcinoma.
- Immunosuppression: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those who have undergone organ transplantation or have HIV/AIDS, are at higher risk.
- Age: Merkel Cell Carcinoma primarily affects older adults, with the average age of diagnosis being in the late 60s to early 70s.
- Fair Skin: People with fair skin, light eyes, and light hair have a higher risk of developing skin cancer, including Merkel Cell Carcinoma.
Rules You Should Know about Tanning
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Symptoms
The most common symptom of Merkel Cell Carcinoma is the appearance of a painless, flesh-colored or bluish-red nodule or lump on the skin. These nodules may grow rapidly and can sometimes ulcerate or bleed. Although Merkel Cell Carcinoma most frequently occurs on sun-exposed areas, it can also develop on other parts of the body, including the trunk and extremities.
Diagnosis
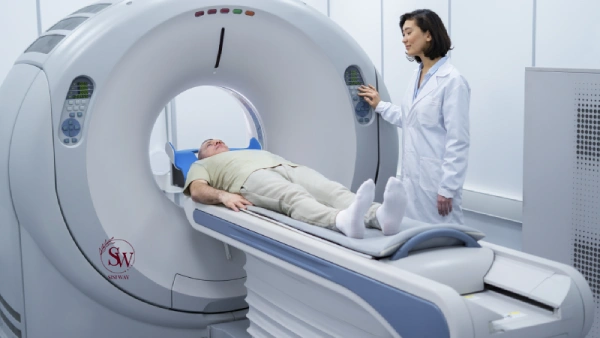
Diagnosing Merkel Cell Carcinoma typically involves a combination of clinical examination, imaging studies, and biopsy. A dermatologist or oncologist may perform a skin biopsy to obtain a tissue sample from the suspicious lesion. This sample is then examined under a microscope by a pathologist to confirm the presence of Merkel Cell Carcinoma.
Additionally, imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be ordered to determine the extent of the disease and whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
Treatment Options
Treatment for Merkel Cell Carcinoma depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. The primary treatment modalities include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor is often the initial treatment for localized Merkel Cell Carcinoma. This may involve excision of the tumor with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete removal.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy may be used before or after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy drugs may be recommended for advanced or metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma to help shrink tumors and slow disease progression.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy drugs, such as checkpoint inhibitors, have shown promising results in treating Merkel Cell Carcinoma by enhancing the body’s immune response against cancer cells.
Prognosis
The prognosis for Merkel Cell Carcinoma varies depending on the stage of the cancer at diagnosis and the individual’s overall health. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. However, Merkel Cell Carcinoma has a higher risk of recurrence and metastasis compared to other types of skin cancer. The five-year survival rate for localized Merkel Cell Carcinoma is approximately 60% to 80%, but this decreases significantly for advanced or metastatic disease.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Jimmy Buffett
In 2011, American singer-songwriter Jimmy Buffett revealed to the public that he had been diagnosed with Merkel Cell Carcinoma. This announcement brought significant attention to this rare form of cancer and raised awareness about the importance of early detection and treatment.

Buffett, known for his laid-back island style and iconic songs such as “Margaritaville,” underwent successful treatment for Merkel Cell Carcinoma. His diagnosis highlighted the fact that skin cancer can affect anyone, regardless of age, lifestyle, or occupation. Buffett’s openness about his experience with Merkel Cell Carcinoma encouraged others to prioritize regular skin checks and take proactive measures to protect themselves from the harmful effects of sun exposure.
Despite facing a health scare, Buffett continued to perform and advocate for skin cancer awareness. His resilience and positive attitude served as an inspiration to many, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a proactive approach to health and well-being.
Buffett’s experience with Merkel Cell Carcinoma underscores the need for increased education and research into skin cancer prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. By sharing his journey publicly, Buffett helped to destigmatize discussions about skin cancer and encouraged individuals to take their skin health seriously.
In summary, Jimmy Buffett’s battle with Merkel Cell Carcinoma brought attention to this rare form of cancer and emphasized the importance of early detection and treatment. His advocacy for skin cancer awareness continues to inspire others to prioritize their health and take proactive measures to protect themselves from the sun’s harmful rays.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Is Merkel Cell Carcinoma hereditary? There is no evidence to suggest that Merkel Cell Carcinoma is directly inherited. However, certain genetic predispositions or mutations may increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing this type of cancer.
2. Can Merkel Cell Carcinoma spread to other parts of the body? Yes, Merkel Cell Carcinoma has the potential to metastasize, or spread, to nearby lymph nodes, as well as distant organs such as the lungs, liver, and bones. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor for any signs of recurrence or metastasis.
3. Are there any preventive measures for Merkel Cell Carcinoma? While it may not be possible to prevent Merkel Cell Carcinoma entirely, reducing exposure to UV radiation by wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and avoiding excessive sun exposure can help lower the risk. Additionally, avoiding immunosuppression and practicing regular skin self-examinations can aid in early detection.
In conclusion, Merkel Cell Carcinoma is a rare but aggressive form of skin cancer that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By raising awareness about the risk factors, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their skin health and improve outcomes in cases of Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Early detection and intervention are key to successful management and long-term survival.